Version Control with Git
0. Introduction
Before We Start
- Create an account at github.com
- Open up a terminal
How This Works
- I’ll work through on my machine and you follow along
- Feel free to ask questions!
- Let me know if I’m going too fast
Exercises
- You do these on your own. When you finish one:
- Offline put a green post-it on your laptop 🟩
- Online 👍 the exercise message in chat
- If you hit a problem:
- Offline put a red post-it note on your laptop 🟥
- Online ✋ raise your hand
1. What is Version Control?
What Does It Do?
- Tracks changes to files
- Any file can be tracked
- Text (
.txt,.csv,.py,.c,.R, etc.) works best- These allow smart diff / merge etc.
Why Use Version Control?
- A more efficient backup
- Reproducibility
Why Use Version Control?
- Sharing
- Teamwork
Version Control Tracks Changes

Version Control Tracks Changes

Version Control Tracks Changes

Version Control Alternatives
- Git
- Distributed
- Subversion (svn)
- Centralised
- Mercurial (hg)
- Distributed
- Git most widely used in academia
- GitHub
- GitLab
Graphical Version Control
| Sourcetree | Git Kraken | Git Desktop |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
GUIs
| PyCharm | RStudio | VS Code |
|---|---|---|
|

|
|
2. Setting Up Git
Key Commands
git config --global user.name "Me"git config --global user.email "me@email.com"git config --global core.editor "nano -w"
Check It Worked
git config --list
user.name=Sam Mangham user.email=mangham@gmail.com core.editor=nano -w [plus much more on Windows]
SSH Key Security
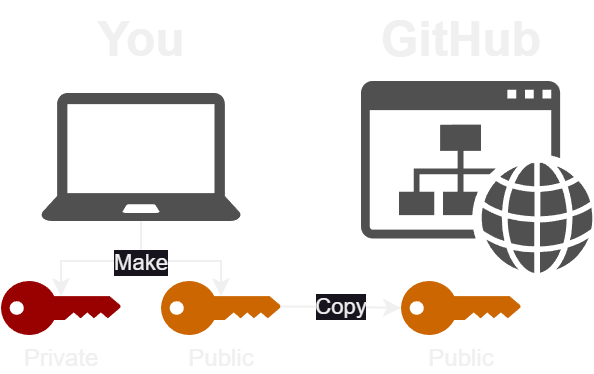
Setting Up GitHub
- Sign up to GitHub: https://github.com/signup
- Open a terminal
ssh-keygen -t ed25519- Accept all the defaults
cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub- Copy the contents to GitHub: https://github.com/settings/ssh/new
- Or use your own if you have one already
Expected Outputs
Generating public/private ed25519 key pair. Enter file in which to save the key (/c/Users/Toaster/.ssh/id_ed25519): Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again: Your identification has been saved in /c/Users/Toaster/.ssh/id_ed25519 Your public key has been saved in /c/Users/Toaster/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub The key fingerprint is: SHA256:<a long string> Toaster@Toast-Nova The key's randomart image is: <a square 'picture'>
Checkpoint ☑️
- Everyone set their name and email?
- Everyone have their SSH key on GitHub?
- Common Problems:
- Copying from the terminal - try right-click -> copy
- Changed the save location for
ssh-keygen
3. Creating a Repository
GitHub Template
- Go to https://github.com/Southampton-RSG-Training/git-novice-template
- “Use This Template”
- Name it
climate-analysis
Key Commands
git clone git@github.com:yourname/climate-analysis- Accept GitHub’s SSH key
cd climate-analysisls -agit status
Expected Outputs
git clone <your repo>
Cloning into 'climate-analysis'... remote: Enumerating objects: 4, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (4/4), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (4/4), done. remote: Total 4 (delta 0), reused 3 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 (from 0) Receiving objects: 100% (4/4), done.
Expected Outputs
git status
# On branch main nothing to commit, working tree clean
Checkpoint ☑️
- Everyone managed to copy and download the template?
- Common Problems:
- Typo in the command (e.g. missing the
:) - SSH key hasn’t been set up
- Not accepting GitHub’s SSH key
- Not used
cdto enterclimate-analysis
- Typo in the command (e.g. missing the
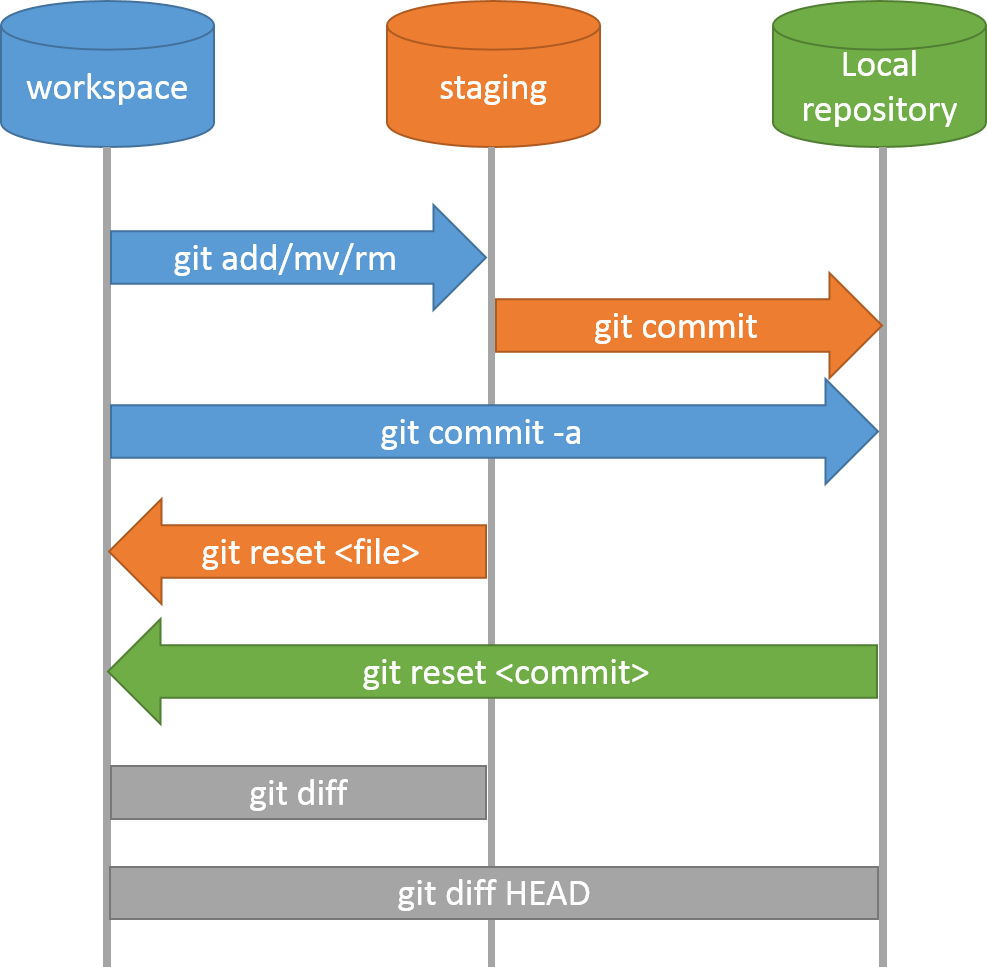
4. Tracking Changes
Key Commands
nano README.mdCtrl-OthenEnterto save,Ctrl-Xto quitgit add README.mdgit statusgit commit -m "Your message"git status
Expected Outputs
git add README.md
If you’re on Windows, you might see:
warning: in the working copy of 'README.md', LF will be replaced by CRLF the next time Git touches it
git commit -m "Your message"
[main 3347109] Added a basic readme file 1 file changed, 4 insertions(+) create mode 100644 README.md
Expected Outputs
git status
On branch main Your branch is ahead of 'origin/main' by 1 commit. (use "git push" to publish your local commits) nothing to commit, working directory clean
Checkpoint ☑️
- Everyone created and committed a readme?
- Everyone have “nothing to commit” in the status?
- Common Problems:
- Stuck in
nano(Ctrl-Oto save,Ctrl-Xto quit) - Didn’t
git add README.md - Forgot the
-mon commit (write your message innano)
- Stuck in
Adding & Committing

Key Commands
git log
Expected Outputs
git log
commit 334710937654821b3a89996c2c6af476548d28e9 (HEAD -> main) Author: Sam Mangham <mangham@gmail.com> Date: Wed Jan 8 18:40:04 2025 +0000 Added a basic readme file commit 3f6b071ef0d35af70793954adb00a3fc7fc7b949 (origin/main, origin/HEAD) Author: Sam Mangham <mangham@gmail.com> Date: Wed Jan 8 18:35:45 2025 +0000 Initial commit
Key Commands
nano climate_analysis.pygit diffgit add climate_analysis.pygit commit -m "Your message"
Expected Outputs
git diff
diff --git a/climate_analysis.py b/climate_analysis.py index 277d6c7..347c42b 100644 --- a/climate_analysis.py +++ b/climate_analysis.py @@ -1,3 +1,5 @@ +"""Tools for analysing climate data files""" + import sys import temp_conversion import signal
git commit
[main 0010185] Add docstring 1 file changed, 2 insertions(+)
Challenge ✏️
- Use
nanoto editclimate_analysis.py - Add “
# TODO: Add rainfall processing code” to the end - Commit the change to the repository
Solution 👁️
nano climate_analysis.pygit diffgit add climate_analysis.pygit commit -m "Your message"
But What Do We Add?
- Code, documentation, configuration files
- For one project or paper
- Usually, not data
- Small common files e.g. tables of atomic weights are OK!
- Anything 10MB+… not really
- Files you can meaningfully compare
- See the Library for data storage
5. Exploring History
Key Commands
git loggit diff HEAD~1 climate_analysis.pygit diff HEAD~2 climate_analysis.py
Expected Outputs
git log
commit ed664c6d480f93829608791f3d8158f2dcab4107 (HEAD -> main) Author: Sam Mangham <mangham@gmail.com> Date: Thu Jan 9 10:11:27 2025 +0000 Added rainfall processing placeholder [3 more commits]
Expected Outputs
git diff HEAD~1 climate_analysis.py
diff --git a/climate_analysis.py b/climate_analysis.py index 347c42b..ce8ef32 100644 --- a/climate_analysis.py +++ b/climate_analysis.py @@ -27,3 +27,6 @@ for line in climate_data: kelvin = temp_conversion.fahr_to_kelvin(fahr) print(str(celsius)+", "+str(kelvin)) + +# TODO: Add rainfall processing code +
Challenge ✏️
- Get the ID of your first commit
- Get a summary of the changes to
climate_analysis.pysince then
Solution 👁️
git log- Take the first 7 characters of the last commit
git diff <COMMIT ID> climate_analysis.py
More Differences

Key Commands
rm climate_analysis.pygit statusgit restore climate_analysis.py- If
restoredoesn’t work, trycheckout
Expected Outputs
git status
On branch main Your branch is ahead of 'origin/main' by 3 commits. (use "git push" to publish your local commits) Changes not staged for commit: (use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed) (use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory) deleted: climate_analysis.py no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
Advanced Use
git checkout <COMMIT ID> climate_analysis.py
Restoring Files

6. Remote Repositories
Local Repo
Remote Backups

Collaboration

Key Commands
git push- Accept GitHub’s SSH key if asked
Expected Output
git push
Counting objects: 11, done. Delta compression using up to 32 threads. Compressing objects: 100% (9/9), done. Writing objects: 100% (9/9), 1.11 KiB | 0 bytes/s, done. Total 9 (delta 2), reused 0 (delta 0) remote: Resolving deltas: 100% (2/2), completed with 1 local object. To git@github.com:smangham/climate-analysis 70bf8f3..501e88f main -> main
Checkpoint ☑️
- Everyone successfully pushed to GitHub?
- Common Problems:
- Cloned with
httpsrather thanssh
- Cloned with
Conflict Creation
Local:
nano README.md- Add your email to the end
git commit -am "Your message"
Remote:
- Go to your repo on GitHub
- Edit
README.mdto add install info to the end - Commit directly to
main
Conflict Creation
git push
Expected Outputs
git push
To git@github.com:smangham/climate-analysis ! [rejected] main -> main (fetch first) error: failed to push some refs to 'git@github.com:smangham/climate-analysis' hint: Updates were rejected because the remote contains work that you do hint: not have locally. This is usually caused by another repository pushing hint: to the same ref. You may want to first merge the remote changes (e.g., hint: 'git pull') before pushing again. hint: See the 'Note about fast-forwards' in 'git push --help' for details.
Checkpoint ☑️
- Everyone managed to edit both the local and remote
mainbranches?
Conflict Resolution
git pullgit config pull.rebase falseif it failsnano README.mdand remove the<<</===/>>>git add README.mdgit commit -am "Your message"git push
Expected Outputs
git pull
remote: Enumerating objects: 5, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (5/5), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done. remote: Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 Unpacking objects: 100% (3/3), done. From github.com:smangham/climate-analysis 501e88f..023f8f6 main -> origin/main Auto-merging README.md CONFLICT (content): Merge conflict in README.md Automatic merge failed; fix conflicts and then commit the result.
Checkpoint ☑️
- Everyone managed to create a conflict, then fix it?
- Common Problems:
- Not committing the changes to your local repo before pulling
- Committing your remote changes to a different branch
Remote Commands
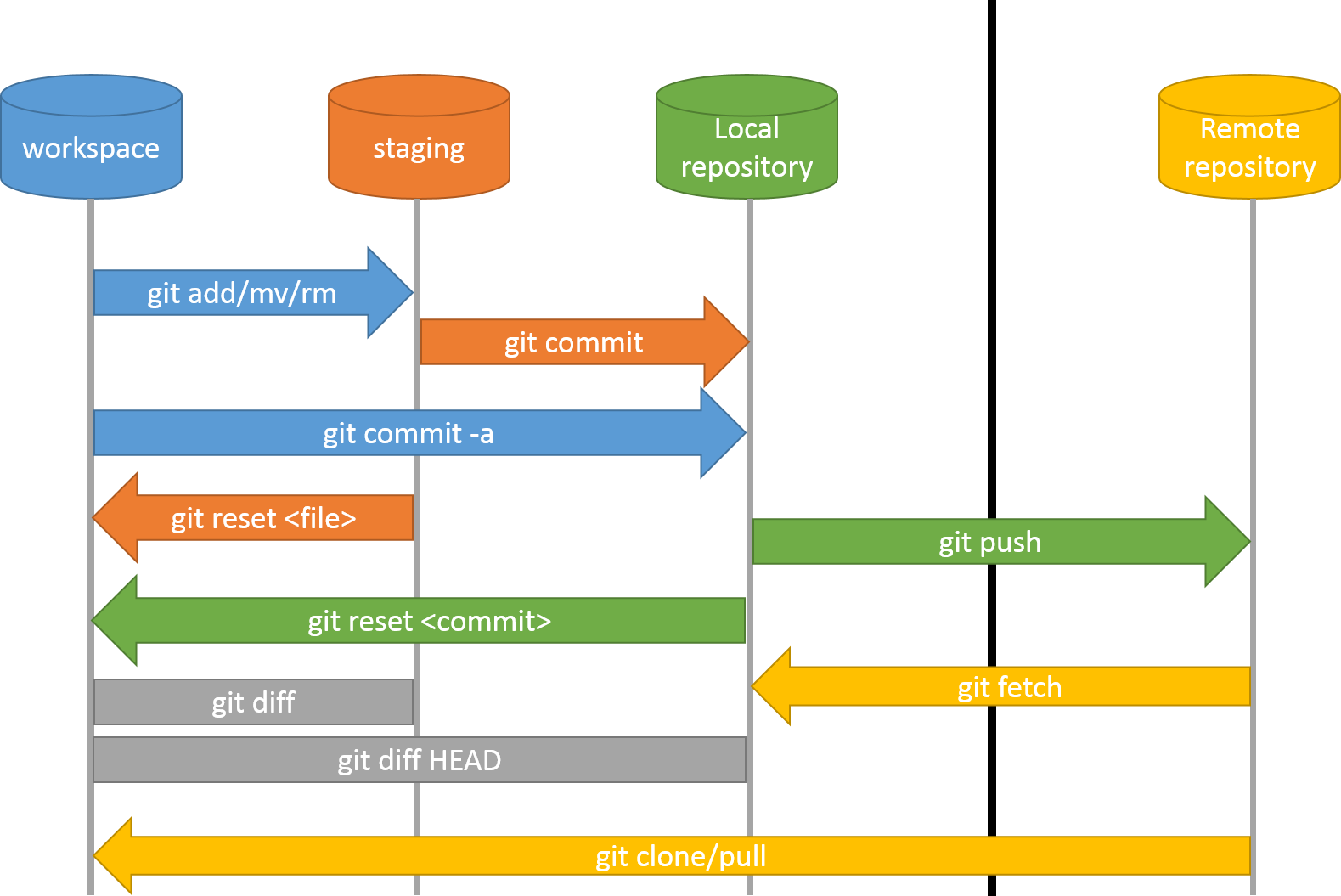
7. Branches
Branching Workflows

Feature Branch

Creating branches
git branchgit branch devgit switch dev- If
switchdoesn’t work, trycheckout
Expected Outputs
git switch dev
Switched to branch `dev`
- If
git switch devdoesn’t work, trygit checkout dev
Branch files
nano rainfall_conversion.pygit add rainfall_conversion.pygit commit -m "Your message"lsgit log
Switching Branches
git switch mainlsgit log
Pushing Branches
git switch devgit push origin devgit config --global push.autoSetupRemote true
Expected Outputs
git push origin dev
Enumerating objects: 25, done. Counting objects: 100% (25/25), done. Delta compression using up to 20 threads Compressing objects: 100% (25/25), done. Writing objects: 100% (25/25), 4.40 KiB | 2.20 MiB/s, done. Total 25 (delta 6), reused 3 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 remote: Resolving deltas: 100% (6/6), done. remote: remote: Create a pull request for 'dev' on GitHub by visiting: remote: https://github.com/smangham/climate-analysis/pull/new/dev remote: To github.com:smangham/climate-analysis * [new branch] dev -> dev
Checkpoint ☑️
- Everyone managed to create and push a branch?
- Common Problems:
- Not pushing to
origin dev - Committing to
mainnotdev
- Not pushing to
Merging Branches
git switch maingit merge dev
8. Ignoring Things
Create Temporary Files
git switch devmkdir resultstouch example.csv results/example.txtgit status
Expected Outputs
git status
On branch dev Your branch is up to date with 'origin/dev'. Untracked files: (use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed) example.csv results/example.txt nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
Create Git Ignore
nano .gitignore- Lines for
*.csvandresults/ git statusgit add .gitignoregit commit -m "Your message"
Expected Outputs
git status
On branch dev Your branch is up to date with 'origin/dev'. Untracked files: (use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed) .gitignore nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)