Remote Desktop Client
In this workshop we will be using remote desktops that come pre-configured with all the resources you will need to complete the course. Prior to that you will need to download the windows remote desktop client suitable for your operating system.
Link to Microsoft’s website, please use the table to pick the link to the app appropriate to your system: Note: For Windows users this is the microsoft store.
The remote desktop will be available to you for the time allocated to your workshop and potentially include some ‘out of hours’ time.
During the course we will have time dedicated to helping you install the software on your own computer so afterwards you can continue to use the skills you have learnt.
Connecting to your remote desktop
- Login to Microsoft Teams using your University account.
- Navigate to the team (Request to join the team if you are not already a member).
- Register for the lab using the provided link, the registration link will be emailed and in the teams channel, register with the same account you use for Teams. You cannot proceed until you have registered.
- Open the Azure Lab Services tab. The labs will start and stop automatically, don’t worry if it is currently stopped.
- You need to copy your RDP information click the three dots in the lower right corner.
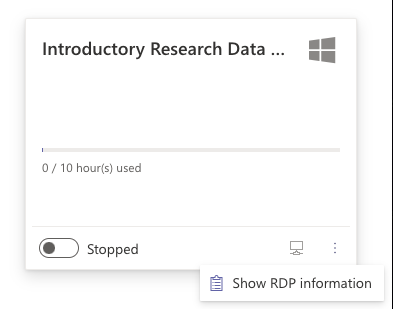
- You will be prompted to copy the remote desktop information copy it to your clipboard.
- Open your remote desktop app that we installed earlier.
- Click on the + and select Add PC, paste in the RDP information. (Green highlights)
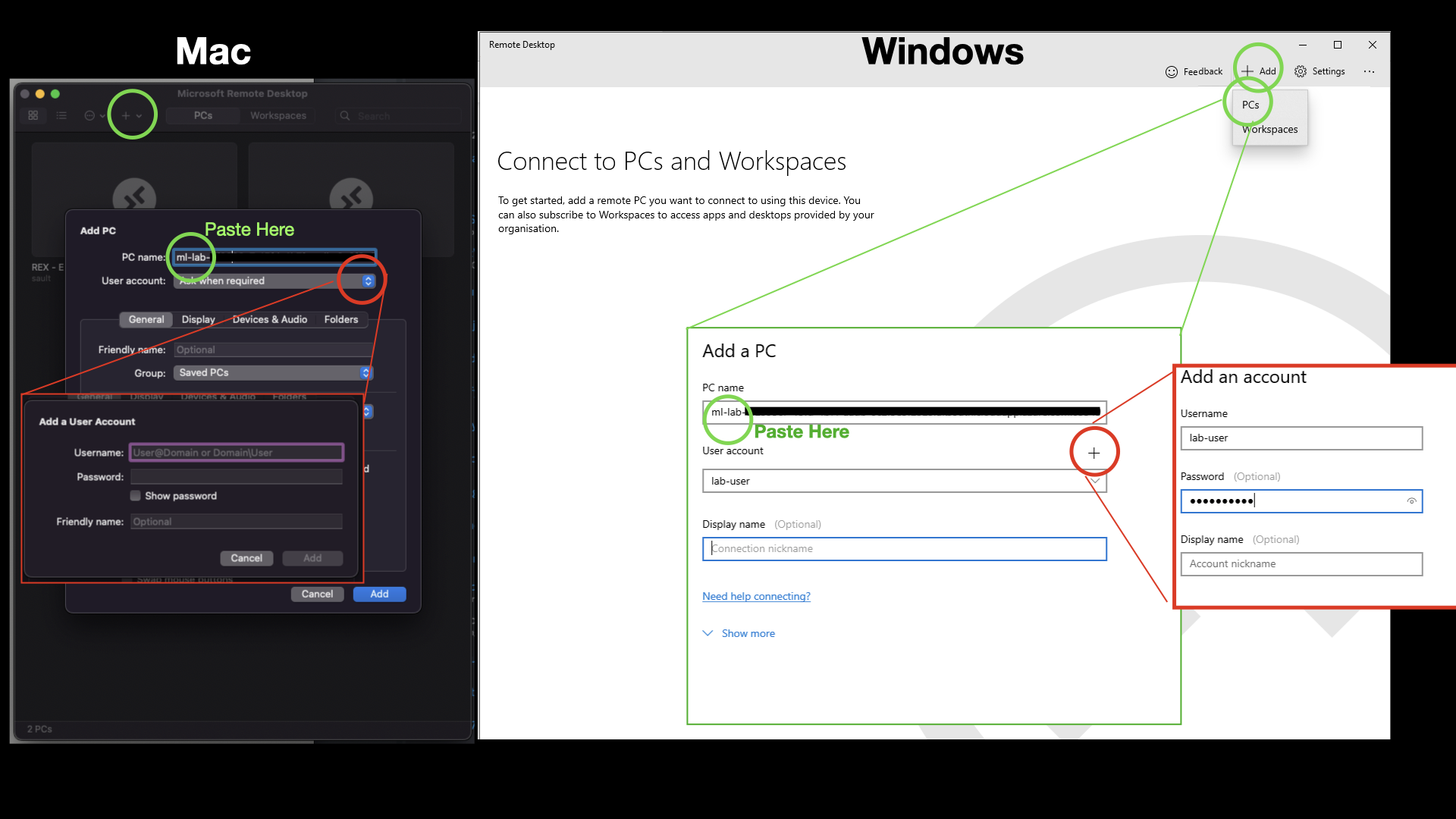
- Optionally add the user account to the PC. The username is ‘lab-user’ the password is ‘Qwerty2000’
Note: the Virtual computers will automatically start before the workshop and stop at the end. If you are inactive for more than 15 minutes, they will also switch off. They can be re-started from the Lab Services Tab but this can take up to 5 minutes, and you may need to ask the instructor. Outside the sessions if you have been allocated additional time you may log in to your session and continue working.
The instructions to install the software on your own computer are provided below.
The Bash Shell
Text Editor
A text editor is the piece of software you use to view and write code. If you have a preferred text editor, please use it. Suggestions for text editors are, Notepad++ (Windows), TextEdit (macOS), Gedit (GNU/Linux), GNU Nano, Vim. Alternatively, there are IDE’s (integrated developer environments) that have more features specifically for coding such as VS Code; there are also IDEs specific to languages will be listed in the appropriate section(s) below.
Open a Terminal
For this lesson, first you need to be able to open a terminal:
- On Windows: run “Git Bash”, to install git bash go here https://gitforwindows.org/ click download and select ‘Git-X.XX.X-64-bit.exe’ from the assets list.
- On Mac OS X: accessed by opening the “Terminal” application, which can be found in the “Utilities” folder which is in your “Applications” folder.
- On Linux: this will depend on the Linux distribution you are running, but you should be able to find a “Terminal” application in your desktop’s application menu.
Git Setup
Windows
We’ll be using Git Bash for both git and a shell to run it in. If you’ve already installed Git Bash then go to the next section. Otherwise, go to git for windows and click Download, then install it. Most of the options can be left on default, but be sure you check these:
- Choosing the default editor used by Git: Make sure Nano is selected from the drop-down. If you’re comfortable with other editors, feel free to change it, but we recommend Nano - we use it as it’s present on Windows, Mac and Linux. If you change it, you might not quite match what we’re doing on-screen.
- Adjusting your PATH environment: Make sure Git from the command line and also from 3rd-party software is selected.
- Choosing HTTPS transport backend: Make sure Use the native Windows Secure Channel Library is selected.
- Configuring the terminal emulator to use with Git Bash: Make sure Use Windows’ default console window is selected.
Mac OS
To use Git you must install the Apple Command Line Tools, this may take a few minutes.
You can obtain these from Apple (requires your Apple ID)
- Select Command Line Tools for Xcode 12 (or higher) and click the link to download the dmg archive.
- If prompted, choose to allow downloads from developer.apple.com
- Open the downloaded dmg archive from the Downloads folder
- Double-click the Command Line Tools.pkg icon to install
Alternatively, you can install the tools from the command line:
$ xcode-select --install
Linux
Git comes pre-installed on most Linux distributions. You can test if it’s installed by running git --version.
If it’s not installed, you can install it by running sudo apt-get install git or sudo yum install git, depending on
your distribution.
GitHub
Later on in the session, we’ll be demonstrating how to share work with collaborators using GitHub. You’ll need to create an account there. As your GitHub username will appear in the URLs of your projects there, it’s best to use a short, clear version of your name if you can.
In addition, we’ll need to set up SSH access to GitHub from your computer. This is how GitHub checks your identity when you try to access it - and is more secure than a password. To set up SSH access, we generate a pair of keys - one public, one private. We want to add the public key to GitHub, whilst the private one stays on our computer.
There are full guides in the GitHub documentation for how to Make an SSH Key and Add an SSH key. However today we have simplified it like so:
If you already have an ssh key you can use it for Github by coping the public key into the clipboard and pasting it into the GitHub settings page.
First we need to create a variable to store your GitHub email. Copy this command, substituting the email you signed up to GitHub with for your_github_email@example.com:
$ my_gh_email=your_github_email@example.com
Then we can run the following command to generate a key-pair and display the public half:
$ ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C $my_gh_email; eval "$(ssh-agent -s)"; ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_ed25519; cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
You will need to press enter a few times to select default options, and set the passphrase to empty.
Copy the last line of output that starts with ssh-ed25519 and ends with your email (it may have gone over multiple lines if your terminal isn’t wide enough).
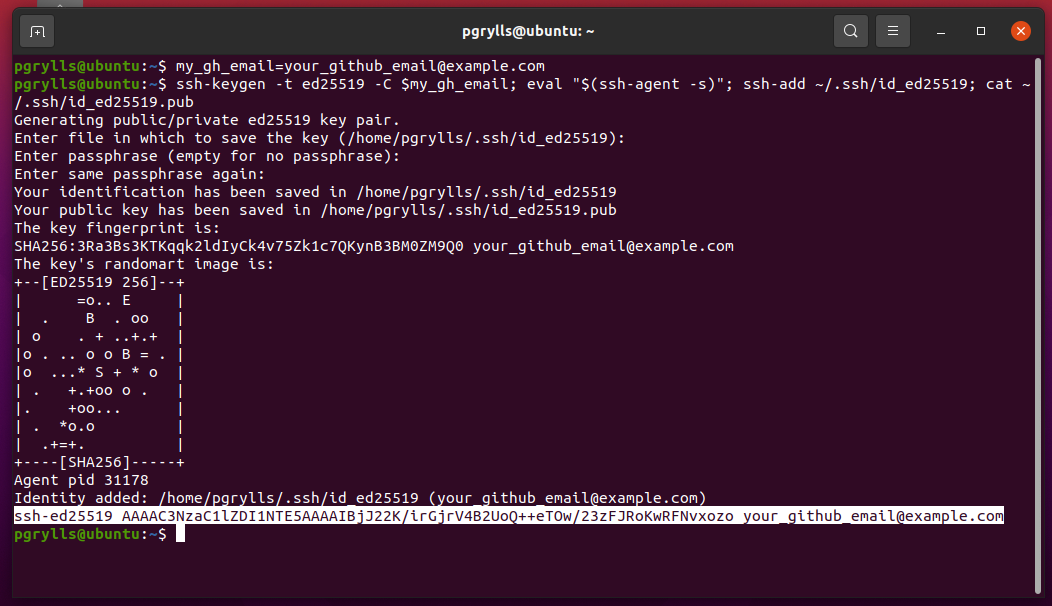
Finally, go to your Settings -> SSH keys page and add a new SSH key (you’ll need to be logged into GitHub with the account you have created). Give the key a memorable name (e.g. the name of the computer you are working on) and paste the key from your clipboard into the box labelled key. Then, click Add SSH key and you’re done!
Download Data for Shell Lesson
Type the following into the prompt that appears (pressing enter/return after each line):
$ cd
$ git clone https://github.com/Southampton-RSG-Training/shell-novice.git
cd will move to your home directory, and git clone will download a copy of the materials.
Alternatively, if you have SSH authentication with GitHub enabled (if you don’t know what this means don’t worry, it is covered in the Git SWC course if you want to know more!) you can use the following:
$ cd
$ git clone git@github.com:Southampton-RSG-Training/shell-novice.git
This should download all the content for the lesson to a new directory. Please let the instructors know if you run into any problems.
Version Control with Git
Download Data for Git Lesson
Now we are ready to download the code that we need for this lesson, using Git on the command line. Open a terminal on your machine, and enter:
$ cd
$ git clone https://github.com/Southampton-RSG-Training/git-novice
cd will move to your home directory, and git clone will download a copy of the materials.
Building Programs with Python
Python Setup
IDEs: PyCharm, Spyder, VS Code
We use Python 3*. The “Anaconda3” package provides everything Python-related you will need for the workshop. To install Anaconda, follow the instructions below.
Some old research projects may be in Python 2 but Python 2 has been retired and new projects should be in Python 3.
Windows
Download the latest Anaconda Windows installer. Double-click the installer and follow the instructions. When asked “Add Anaconda to my PATH environment variable”, answer “yes”. It will warn you not to, but it’s required for it to be found by git bash After it’s finished, close and reopen any open terminals to reload the updated PATH and allow the installed Python to be found.
Once the Anaconda installation is finished you will be asked if you want the installer to initialize Anaconda3 by running conda init? You should select yes. Alternatively/additionally you will need to run the following command in GitBash
conda init bash
Then close and reopen GitBash.
Please test the python install open GitBash (or your favorite terminal) and run the following command to verify that the installation was successful.
cd ~
python
You can then type the following to exit:
quit()
In some cases GitBash will hang on this command and not launch the Python interpreter.
In this case close and reopen git bash and issue the following commands:
cd ~
echo 'alias python="winpty python.exe"' >> .bashrc
source .bashrc
python
Mac OS X
Mac OS Intel
Download the latest Anaconda Mac OS X installer. Double-click the .pkg file and follow the instructions.
Mac OS M1
If you have a M1 Mac you need a specific version of Anaconda follow the link below.
Once the Anaconda installation is finished you will be asked if you want the installer to initialize Anaconda3 by running conda init? You should select yes.
Linux
Download the latest Anaconda Linux Installer.
Install via the terminal like this (you will need to change the version number to the latest version):
First move to the folder where you downloaded the installer, this is likely to be the Downloads folder e.g.
$ cd ~/Downloads
$ bash Anaconda3-2021.11-Linux-x86_64.sh
Answer ‘yes’ to allow the installer to initialize Anaconda3 in your .bashrc.
Download Data for Python Lesson
Now we are ready to download the code that we need for this lesson. Open a terminal on your machine, and enter:
$ cd
$ git clone https://github.com/Southampton-RSG-Training/python-novice
cd will move to your home directory, and git clone will download a copy of the materials.